Most Recent Fortinet NSE6_FSW-7.2 Exam Dumps
Prepare for the Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiSwitch 7.2 exam with our extensive collection of questions and answers. These practice Q&A are updated according to the latest syllabus, providing you with the tools needed to review and test your knowledge.
QA4Exam focus on the latest syllabus and exam objectives, our practice Q&A are designed to help you identify key topics and solidify your understanding. By focusing on the core curriculum, These Questions & Answers helps you cover all the essential topics, ensuring you're well-prepared for every section of the exam. Each question comes with a detailed explanation, offering valuable insights and helping you to learn from your mistakes. Whether you're looking to assess your progress or dive deeper into complex topics, our updated Q&A will provide the support you need to confidently approach the Fortinet NSE6_FSW-7.2 exam and achieve success.
The questions for NSE6_FSW-7.2 were last updated on May 4, 2025.
- Viewing page 1 out of 11 pages.
- Viewing questions 1-5 out of 55 questions
Exhibit.
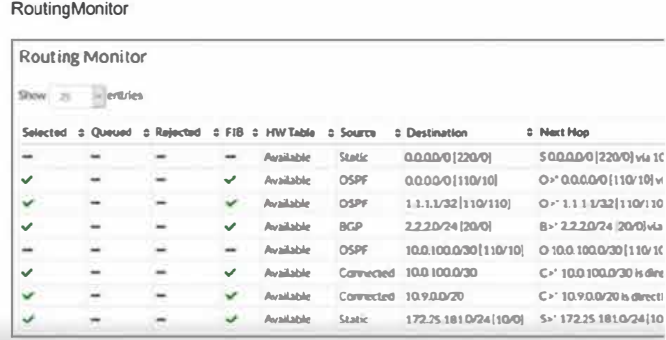
Two routes are not installed in the forwarding information base (FIB) as shown in the exnibit. Which two statements about these two route entries are true? (Choose two.)
From the exhibit and the details given about the routes not installed in the FIB:
These two routes have a higher administrative distance value available to the destination networks (Option A): Administrative distance is a measure used by routers to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from two different routing protocols. A higher administrative distance means that the route is considered less trustworthy, thus not selected for the FIB unless the more preferred routes fail.
These two routes will become primary, if the best routes are removed (Option B): In routing, if the currently installed routes (which are considered the best due to reasons like lower administrative distance) are removed or become unavailable, the next best routes based on administrative distance will be used. This behavior ensures redundancy and maintains network connectivity in diverse scenarios.
This approach is aligned with standard routing protocol behavior as documented in networking protocols and Fortinet's routing mechanisms which prioritize routes based on administrative distance and other metrics to maintain efficient and reliable network routing.
Exhibit.

The exhibit shows the current status of the ports on the managed FortiSwitch.
Access-1.
Why would FortiGate display a serial number in the Native VLAN column associated with the port23 entry?
The appearance of a serial number in the Native VLAN column for port23 suggests that the switch connected to this port is identified uniquely in the network. Given the options provided:
A standalone switch with the shown serial number is connected on port23 (Option C): This is the most plausible explanation. The FortiSwitch configuration interface is displaying the serial number of a standalone switch that is directly connected to port23. This kind of display helps in identifying and managing individual devices in a network setup, especially in environments with multiple switches.
Which packet capture method allows FortiSwitch to capture traffic on trunks and management interfaces?
FortiSwitch supports packet capture through various methods, but the Sniffer profile is specifically capable of capturing traffic on both trunks and management interfaces. Here's why:
Sniffer Profile (B):
Versatile Capture: The sniffer profile in FortiSwitch is designed to capture traffic across different types of interfaces, including trunks (where multiple VLANs are present) and management interfaces (used for controlling and monitoring the switch).
Configuration Flexibility: You can configure sniffer profiles to target specific traffic, offering flexibility in monitoring and troubleshooting network issues on both data and management planes.
Other Options:
SPAN (A) is used mainly for mirroring traffic to another port for analysis but is typically limited in its ability to capture management interface traffic.
sFlow (C) and TCP dump (D) are useful tools but do not specifically align with the capability to universally capture traffic across trunks and management interfaces in the context described.
How is traffic routed on FortiSwitch?
Layer 3 routing can be configured on FortiSwitch, while managed by FortiGate (D): FortiSwitch, when managed by FortiGate, supports Layer 3 routing capabilities. This allows for routing between VLANs directly on the switch, enhancing network efficiency by reducing the need to pass traffic through higher network layers for inter-VLAN communication. This configuration enables more sophisticated network setups and efficient routing directly at the switch level.
Which two statements about 802.1X authentication on FortiSwitch ports are true? (Choose two.)
All hosts behind an authenticated port are allowed access after a successful authentication (A): Once a device on a port successfully authenticates using 802.1X, all other devices connected behind that port also gain network access. This is typical in scenarios where a switch is behind an authenticated port and not each device individually authenticates.
All devices connecting to FortiSwitch must support 802.1X authentication (D): For a network secured with 802.1X, all devices attempting to connect through the FortiSwitch must support and participate in 802.1X authentication to gain access. This ensures that all devices on the network are authenticated before they are allowed to communicate on the network.
Unlock All Questions for Fortinet NSE6_FSW-7.2 Exam
Full Exam Access, Actual Exam Questions, Validated Answers, Anytime Anywhere, No Download Limits, No Practice Limits
Get All 55 Questions & Answers