Most Recent HPE6-A84 Exam Dumps
Prepare for the HP Aruba Certified Network Security Expert Written Exam exam with our extensive collection of questions and answers. These practice Q&A are updated according to the latest syllabus, providing you with the tools needed to review and test your knowledge.
QA4Exam focus on the latest syllabus and exam objectives, our practice Q&A are designed to help you identify key topics and solidify your understanding. By focusing on the core curriculum, These Questions & Answers helps you cover all the essential topics, ensuring you're well-prepared for every section of the exam. Each question comes with a detailed explanation, offering valuable insights and helping you to learn from your mistakes. Whether you're looking to assess your progress or dive deeper into complex topics, our updated Q&A will provide the support you need to confidently approach the HPE6-A84 exam and achieve success.
The questions for HPE6-A84 were last updated on May 2, 2025.
- Viewing page 1 out of 12 pages.
- Viewing questions 1-5 out of 60 questions
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an Aruba ClearPass cluster. The customer has AOS-CX switches that implement 802.1X authentication to ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM).
Switches are using local port-access policies.
The customer wants to start tunneling wired clients that pass user authentication only to an Aruba gateway cluster. The gateway cluster should assign these clients to the ''eth-internet" role. The gateway should also handle assigning clients to their VLAN, which is VLAN 20.
The plan for the enforcement policy and profiles is shown below:
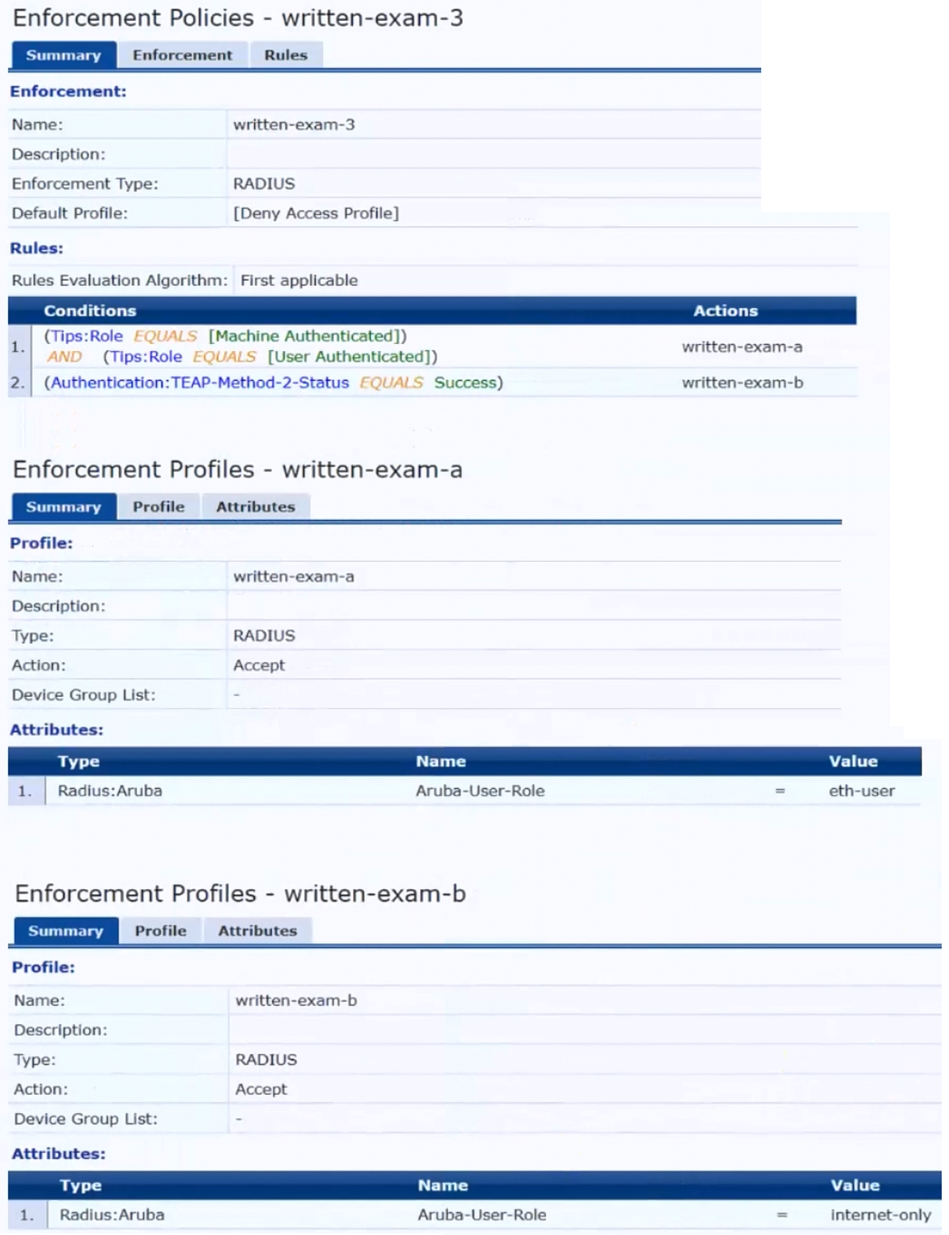
The gateway cluster has two gateways with these IP addresses:
* Gateway 1
o VLAN 4085 (system IP) = 10.20.4.21
o VLAN 20 (users) = 10.20.20.1
o VLAN 4094 (WAN) = 198.51.100.14
* Gateway 2
o VLAN 4085 (system IP) = 10.20.4.22
o VLAN 20 (users) = 10.20.20.2
o VLAN 4094 (WAN) = 198.51.100.12
* VRRP on VLAN 20 = 10.20.20.254
The customer requires high availability for the tunnels between the switches and the gateway cluster. If one gateway falls, the other gateway should take over its tunnels. Also, the switch should be able to discover the gateway cluster regardless of whether one of the gateways is in the cluster.
Assume that you have configured the correct UBT zone and port-access role settings. However, the solution is not working.
What else should you make sure to do?
The correct answer is B. Create a new VLAN on the AOS-CX switch and configure that VLAN as the UBT client VLAN.
The other options are not correct or relevant for this issue:
Option C is not correct because VIA licenses are not required for UBT. VIA licenses are required for enabling VPN services on Aruba Mobility Controllers for remote access clients using Aruba Virtual Intranet Access (VIA) software . VIA licenses are not related to UBT or wired clients.
Option D is not correct because changing the port-access auth-mode mode to client-mode on any edge ports to which tunneled clients might connect would not affect UBT. The port-access auth-mode mode determines how a port handles authentication requests from multiple clients connected to a single port . Client-mode is the default mode that allows only one client per port, while multi-client-mode allows multiple clients per port. The port-access auth-mode mode does not affect how UBT works or how traffic is tunneled from a port.
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is migrating from on-prem AD to Azure AD as its sole domain solution. The customer also manages both wired and wireless devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune).
The customer wants to improve security for the network edge. You are helping the customer design a ClearPass deployment for this purpose. Aruba network devices will authenticate wireless and wired clients to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster (which uses version 6.10).
The customer has several requirements for authentication. The clients should only pass EAP-TLS authentication if a query to Azure AD shows that they have accounts in Azure AD. To further refine the clients' privileges, ClearPass also should use information collected by Intune to make access control decisions.
The customer wants you to configure CPPM to collect information from Intune on demand during the authentication process.
What should you tell the Intune admins about the certificates issued to clients?
The certificates issued to clients do not need to be issued by a well-known, trusted CA, as long as ClearPass trusts the CA that issued them. The certificates do not need to include the client MAC address in the subject name, as this is not relevant for querying Intune. The certificates do not need to be issued by a ClearPass Onboard CA, as this is not a requirement for using the Intune extension.
A customer has an AOS 10 architecture, consisting of Aruba AP and AOS-CX switches, managed by Aruba Central. The customer wants to obtain information about the clients, such as their general category and OS.
What should you explain?
Aruba Central can provide visibility and profiling of clients using the Client Insights feature, which is an AI-powered solution that uses native infrastructure telemetry to identify and classify clients based on their OS and general category. This feature does not require any additional hardware or software, such as gateways, IP helpers, or packet sniffers. It works by collecting and analyzing data from the Aruba APs and AOS-CX switches that are managed by Aruba Central. You can find more information about Client Insights in the Visibility and profiling solutions | HPE Aruba Networking page and the Clients Profile - Aruba page.
Refer to the exhibit.
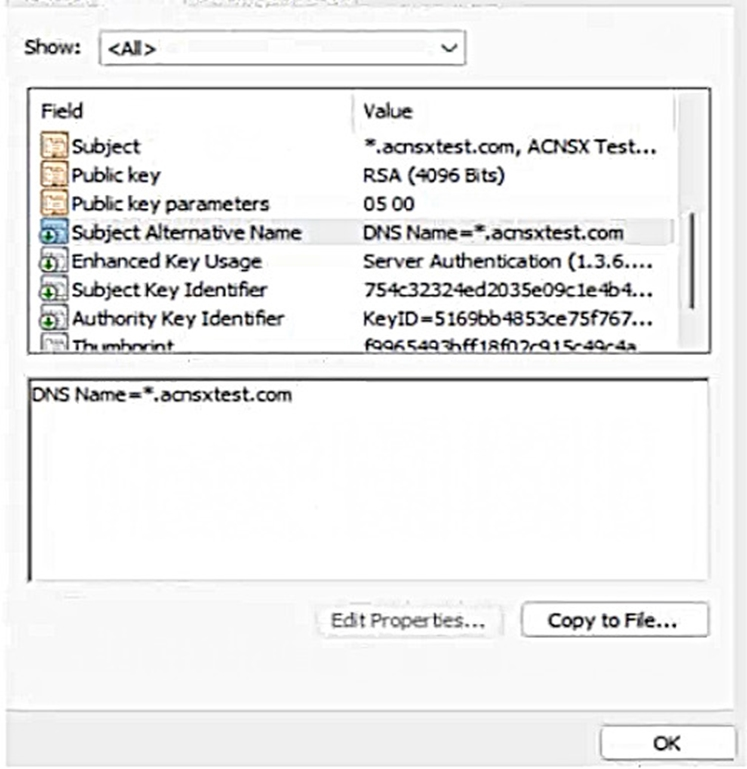
You have been given this certificate to install on a ClearPass server for the RADIUS/EAP and RadSec usages.
What is one issue?
The exhibit shows a screenshot of a certificate that has the following information:
The subject common name (CN) is *.clearpass.local, which is a wildcard domain name that matches any subdomain under clearpass.local.
The subject alternative names (SANs) are DNS Name=clearpass.local and DNS Name=*.clearpass.local, which are the same as the subject CN.
The issuer CN is clearpass.local, which is the same as the subject domain name.
The key usage (KU) is Digital Signature and Key Encipherment, which are required for RADIUS/EAP and RadSec usages.
The extended key usage (EKU) is Server Authentication and Client Authentication, which are also required for RADIUS/EAP and RadSec usages.
The issue with this certificate is that it uses a fully qualified the '.local' domain name, which is a reserved domain name for local networks that cannot be registered on the public Internet. This means that the certificate cannot be verified by any public certificate authority (CA), and therefore cannot be trusted by any external devices or servers that communicate with ClearPass. This could cause problems for RADIUS/EAP and RadSec usages, as they rely on secure and authenticated connections between ClearPass and other devices or servers.
To avoid this issue, the certificate should use a valid domain name that can be registered on the public Internet, such as clearpass.com or clearpass.net. This way, the certificate can be issued by a public CA that is trusted by most devices and servers, and can be verified by them. Alternatively, if the certificate is intended to be used only within a private network, it should be issued by a private CA that is trusted by all devices and servers within that network.
Refer to the scenario.
A customer requires these rights for clients in the ''medical-mobile'' AOS firewall role on Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs):
External devices should not be permitted to initiate sessions with ''medical-mobile'' clients, only send return traffic.
The line below shows the effective configuration for the role.
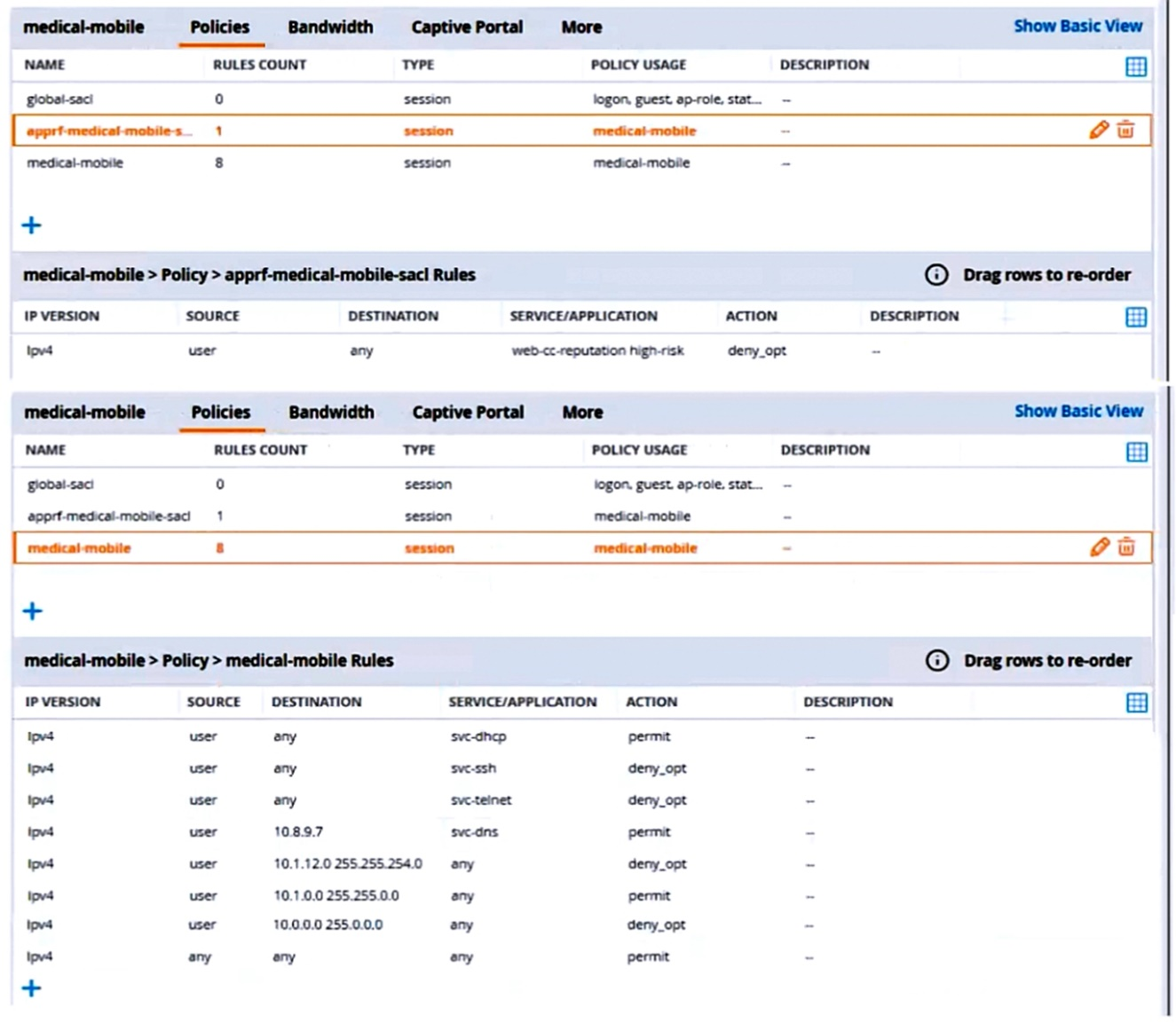
There are multiple issues with this configuration. What is one change you must make to meet the scenario requirements? (In the options, rules in a policy are referenced from top to bottom. For example, ''medical-mobile'' rule 1 is ''ipv4 any any svc-dhcp permit,'' and rule 6 is ''ipv4 any any any permit'.)
Unlock All Questions for HP HPE6-A84 Exam
Full Exam Access, Actual Exam Questions, Validated Answers, Anytime Anywhere, No Download Limits, No Practice Limits
Get All 60 Questions & Answers