Most Recent ISTQB CTAL-TM Exam Dumps
Prepare for the ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level Test Management v3.0 exam with our extensive collection of questions and answers. These practice Q&A are updated according to the latest syllabus, providing you with the tools needed to review and test your knowledge.
QA4Exam focus on the latest syllabus and exam objectives, our practice Q&A are designed to help you identify key topics and solidify your understanding. By focusing on the core curriculum, These Questions & Answers helps you cover all the essential topics, ensuring you're well-prepared for every section of the exam. Each question comes with a detailed explanation, offering valuable insights and helping you to learn from your mistakes. Whether you're looking to assess your progress or dive deeper into complex topics, our updated Q&A will provide the support you need to confidently approach the ISTQB CTAL-TM exam and achieve success.
The questions for CTAL-TM were last updated on May 5, 2025.
- Viewing page 1 out of 36 pages.
- Viewing questions 1-5 out of 178 questions
You are monitoring the test results for the first week of system test execution to ensure they conform to the test plan objectives. You are guided by the list of test conditions and traceability matrix produced following test design. Test Plan objectives
* Approach - Risk-based and depth first
* Status reporting - Execution statuses must be either "Passed*, "Failed", "Blocked" or "Not Run"
* Traceability - Test execution results must be traceable back to the test conditions
Test Conditions
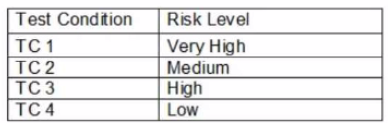
Traceability matrix
Which one of the following is a correct statement regarding the current status of test plan objectives?
SELECT ONE OPTION
You are working on a project that is having problems with regressions. With each release of software given to the test team. 50% of the defects found are actually regressions. To combat this you have decided to implement test automation. You have given your automation team the following goal
'Implement lest automation to automate 90% of the manual regression tests before the product release date.''
Which of the following is likely an issue with this goal being defined as "SMART?
Understanding SMART Goals:
SMART goals must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
The goal 'automate 90% of the manual regression tests before the product release date' may not be achievable depending on the time constraints and resources available.
Evaluation of Options:
A is correct because the issue lies in whether automating 90% is feasible within the timeline.
B is incorrect as the goal is specific.
C is incorrect because automating regression tests is relevant to reducing regressions.
D is incorrect since the goal is measurable by the percentage of automation achieved.
Reference and Syllabus Alignment:
Aligned with ISTQB Advanced Test Management guidelines on goal setting and test automation strategies (TM-1.6.2).
You have directed one of your testers to construct a "smoke test" to execute against new builds prior to starting formal testing. This is an example of which software development lifecycle activity?
[1]
You have assembled the following cost of quality numbers 1 000 defects were found prior to release and 100 were found after.

Given this information what should you conclude?
Cost of Quality Analysis:
The given table lists costs for defect prevention, appraisal, internal failure, and external failure.
Defect prevention cost is $50,000, while costs for appraisal, internal failures, and external failures are $250,000, $200,000, and $200,000, respectively.
The combined cost of internal and external failures is significantly high compared to defect prevention costs.
Defect Detection and Prevention (DDP):
DDP measures the effectiveness of defect prevention activities and early detection mechanisms.
In this case, 1,000 defects were caught before release (appraisal) and 100 defects escaped to production.
DDP = (Defects found before release / Total defects) = 1000 / (1000 + 100) = 90.91%.
While this DDP is relatively high, the costs of appraisal and failures indicate that prevention strategies need more investment.
Key Cost Drivers:
High internal and external failure costs indicate inefficiencies in earlier stages of quality assurance.
Shifting investments from appraisal and failure costs towards defect prevention would reduce the overall cost of quality.
Evaluating Options:
Option A ('More testing needed because DDP < 90%') is invalid since DDP is above 90%.
Option C ('The cost of testing is justified') does not address the imbalance between high failure costs and low prevention spending.
Option D ('More effort on appraisal') contradicts the cost-benefit focus of investing in prevention.
Option B is correct because enhancing defect prevention strategies will reduce downstream costs.
Reference and Syllabus Alignment:
This conclusion aligns with the ISTQB Advanced Test Management syllabus section on 'Cost of Quality' and strategies to optimize testing investments. Specifically, prevention is emphasized as more cost-effective than appraisal and failure management.
Your team has been assigned to lest a new product that is tightly integrated with existing systems The integrations include data transfers and transformations You have access to the architectural design documents and the integration specifications and some of your testers are former developers.
Given this information, what is the most appropriate test approach?
Context Analysis:
The scenario involves tight integration, architectural design, and data transformations, requiring detailed and structured approaches.
Access to architectural documents and experienced testers (former developers) aligns with model-based and white-box techniques.
Evaluation of Options:
A . Model-based and white-box:
Correct. Model-based testing leverages design documents, while white-box testing uses internal knowledge for detailed integration testing.
B . Experience-based and black-box:
Incorrect. This is less structured and doesn't utilize available design documentation or tester expertise.
C . Risk-based and non-functional:
Incorrect. Risk-based testing focuses on high-priority areas but doesn't leverage the design documents for integration specifics.
D . Requirements-based and functional:
Incorrect. While functional testing is relevant, requirements-based testing does not utilize internal system knowledge effectively.
Syllabus Alignment:
ISTQB emphasizes model-based and white-box testing as appropriate for systems with complex integrations (TM-1.2.6).
ISTQB Advanced Level Test Management Syllabus (TM-1.2.6)
Unlock All Questions for ISTQB CTAL-TM Exam
Full Exam Access, Actual Exam Questions, Validated Answers, Anytime Anywhere, No Download Limits, No Practice Limits
Get All 178 Questions & Answers